?To address the spread of monkeypox, three states have declared a public health state of emergency and the federal government is expected to follow suit. The disease can be transmitted through skin-to-skin contact, but not by sharing office space and talking with co-workers. We’ve rounded up SHRM Online resources and news articles from other trusted outlets.
California, Illinois and New York have declared a public health state of emergency over the spreading of monkeypox. Those three states—home to the nation’s three largest cities—have reported more than 45 percent of all confirmed monkeypox infections in the United States. The country has reported more than 6,000 cases of monkeypox across 48 states, Washington, D.C., and Puerto Rico.
(U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)
California Takes Action
California’s governor declared a state of emergency to speed efforts to combat the monkeypox outbreak. Gov. Gavin Newsom said the declaration will help California coordinate a governmentwide response, seek more vaccines and lead outreach and education efforts on where people can get treatment and vaccination.
Cities Step Up
New York City and San Francisco have declared a local public health emergency. Vaccinations to help control the spread of the disease have been in short supply.
(Politico)
Federal Action Expected
The Biden administration reportedly plans to declare a public health emergency, according to a federal official familiar with the discussions.
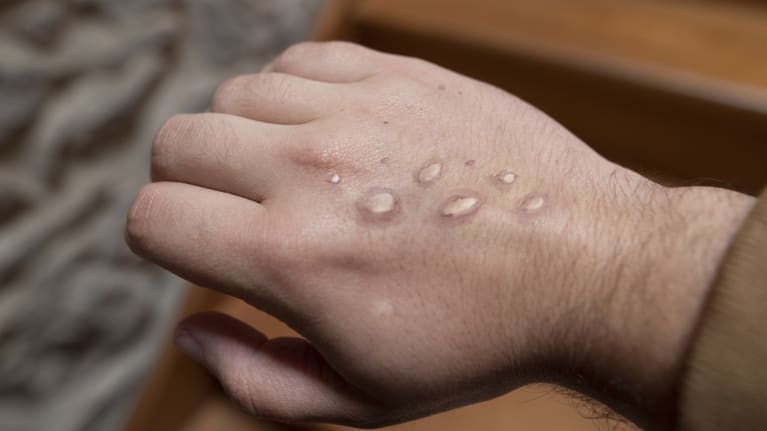
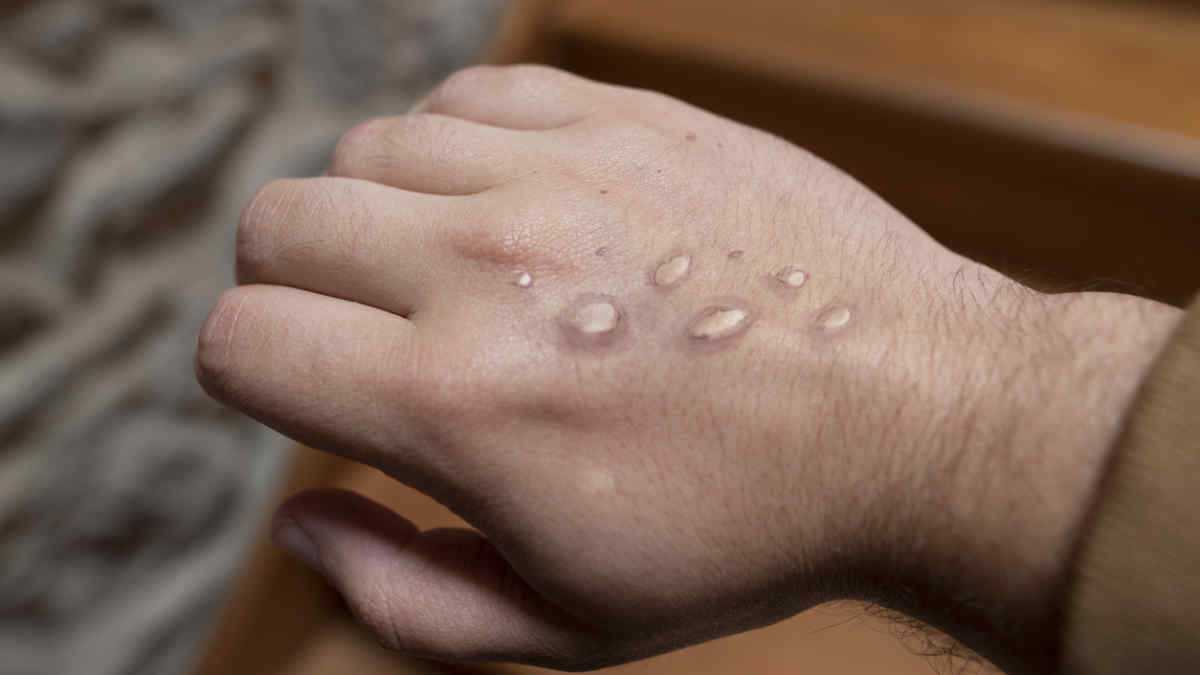
How It Spreads
Monkeypox is spread through close contact with someone who has symptoms or by touching items that touched the infectious rash or body fluids, such as unwashed bedding and towels, or sharing cups and plates that came in contact with the infectious rash or body fluids. It is not transmitted via casual, brief conversations or walking by someone.
WHO Calls Monkeypox Emergency
On July 23, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared monkeypox a “public health emergency of international concern.” Employers should review information provided by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the WHO, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, and the U.S. Department of State. Employers should remind employees about precautions to prevent monkeypox infections, such as washing your hands often, using an alcohol-based hand sanitizer, routinely cleaning frequently touched surfaces, avoiding skin-to-skin contact with people who have a rash, and staying at home when you are sick.
(K&L Gates law firm)